How To Remove Acetaldehyde From Body Naturally

⏱️ TL:DR ∙ Article in 20s
Acetaldehyde is a common toxin we’re all exposed to from alcohol, smoke, and foods. It damages DNA and increases cancer risk, especially in those lacking the ALDH2 enzyme. While exposure should be avoided whenever possible, over the counter supplements like glutathione, NAC, quercetin, and L-theanine, neutralize toxins, aid detoxification. Sunset combines NAC, quercetin, L-theanine to effectively help remove acetaldehyde from body, reducing health risks and keeping levels low.
Action items:
- What is acetaldehyde?
- Sources of acetaldehyde
- Removing acetaldehyde naturally
- Who is at risk?
- Scientific methods to remove acetaldehyde
Share this article
Copy and paste this link
Do you ever experience headaches, congestion, a red face when you drink alcohol or other unpleasant reactions? If so, you may have a sensitivity to sulfites or histamines, common additives used in many alcoholic beverages. The good news is that with the right information (and maybe some something you can take to help with the symptoms), you can enjoy alcohol again without negative effects.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explain exactly what sulfites and histamines are, why they cause problems for some people, and most importantly, which types of alcohol you can safely drink to avoid reactions. We've done the research so you can relax and savor drinks that mesh with your body chemistry and sensitivities.
Whether you want to prevent headaches from red wine, congestion from beer, or other symptoms, we have the tips and product recommendations you need to raise a glass without worry. Let's get started on determining your ideal alcohol-without-histamine cocktail!
What is Acetaldehyde?
Acetaldehyde is a flammable liquid that is commonly used in the manufacture of acetic acid, perfumes, and flavors.[1] It is also found in varying concentrations in plants, fresh fruits, vegetables, cigarette smoke, gasoline and diesel exhaust fumes.[2]
In addition to the above-mentioned sources, our bodies also encounter the toxin during the metabolism of alcohol. Acetaldehyde is produced via the action of alcohol dehydrogenase on ethanol and is often stated to be a lot more toxic than ethanol itself.[3]
Sources of Acetaldehyde
In order to help break down acetaldehyde, it is important to know how it is getting into the body. Here are some common ways that acetaldehyde makes its way from the environment into the human body:
Acetaldehyde from Alcohol
As mentioned above, acetaldehyde produced by the action of alcohol dehydrogenase when we consume alcohol.
Alcohol dehydrogenases are a class of enzymes that play an important role in the oxidation and reduction of various aldehydes such as acetaldehyde. These enzymes occur in large numbers in the liver and play an important role in metabolising the alcohol that we consume.[4]
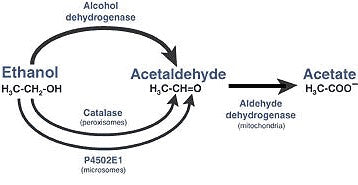
They do this by breaking apart the alcohol molecule to allow the body to more easily eliminate it. Firstly, alcohol dehydrogenase enzymes convert the alcohol to acetaldehyde. Then the acetaldehyde is further broken down into a less toxic byproduct called acetate. The acetate is then easily converted into water and carbon dioxide for easy elimination by the body.[5]
Acetaldehyde from Smoking
Tobacco smoke has been shown to contain acetaldehyde, which absorbs into the body via the upper respiratory tract and mouth. Acetaldehyde also gets dissolved into saliva and enters the stomach when it is swallowed.[6] Once it enters the body, it is broken down by aldehyde dehydrogenase in the blood, liver and elsewhere in the body, including at the blood-brain barrier.[7]
Some studies have shown that naturally occurring polysaccharides in tobacco, like cellulose, are the main sources of acetaldehyde in cigarette smoke.[8] The amount that enters the body is mostly affected by design factors that increase total smoke production such the kinds of filter and paper used.
Acetaldehyde from Air Pollution
Acetaldehyde also finds common use in industry. This can result in varying quantities of it finding its way into waste water and the air that we breath. Some common sources of acetaldehyde from industry include emissions from power plants, refineries, cement kilns, lumber and wood mills and paper mills. Aside from industrial sources, another dominant source of acetaldehyde is the smoke from wood burning in residential fire places and the controlled burning of forests and vegetation.[9]
Acetaldehyde is also found in automobile and diesel exhaust fumes, making it prevalent in the air of densely populated cities.
Acetaldehyde from Diet
To further emphasise the prevalence of acetaldehyde in our environment, it is also necessary point out the degree to which this toxin enters our body through the foods and beverages we consume. Like any toxin, the extent of its deleterious effect on the body is proportional to the regularity of our exposure to it.
Below is a chart taken from a 2011 study conducted by German researchers that looked at the amount of acetaldehyde exposure we get from various good groups:[10]
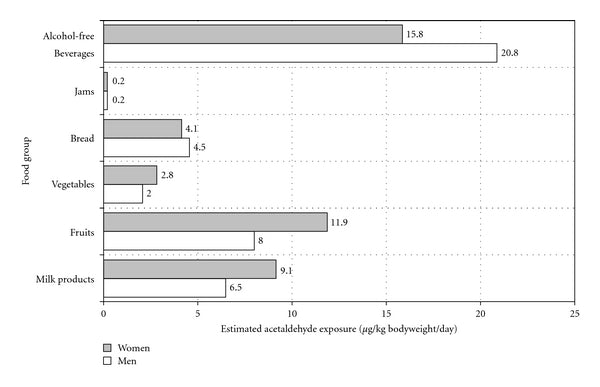
In this study, some of the foods and beverages containing the highest amount of acetaldehyde included instant coffee and fermented foods such as yogurt.
Acetaldehyde is a by-product of the fermentation process, thus most fermented foods and beverages such as yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, natto and kombucha, will contain elevated levels of acetaldehyde.
In most cases, the fermentation of the foods and beverages we consume occurs outside of the body. However, in the case of sugars, it is common for fermentation to occur inside of our digestive system (by a yeast called Candida Albicans). In this case, the amount of acetaldehyde exposure can depend on the amount of sugar consumed and the prevalence of Candida Albicans in an individual’s internal bacterial ecosystem.[11]
Learn How To Remove Acetaldehyde From Body Naturally
Why is it so important to learn how to remove acetaldehyde from body naturally? Here's why:
As evidenced above, acetaldehyde can make its way into the body from a plethora of different sources in our environment. As alarming as this might sound, it is necessary to preface this with the notion that it is not exposure per se that is harmful, but rather the scale and regularity of this exposure.
The higher the quantity of acetaldehyde that enters the system, the harder it will be for the body to adequately break it down into a non-toxic and readily excretable form. Similarly, the regularity of this exposure will also be relevant in terms of how well the body can catalyze its various defenses to neutralize the toxin.
In cases where the body is unable to adequately break down acetaldehyde into a non-harmful and readily excretable form (i.e. due to ALDH2 deficiency), the toxin can enter the blood and cause various health complications.
DNA Damage
In a recent 2018 study conducted by researchers from the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology at Cambridge, researchers confirmed a link between acetaldehyde and damage to DNA in blood stem cells. They also found that some subjects (i.e. those with ALDH2 deficiency) were subject to 4 times more DNA damage than subjects without the deficiency.[12]
Cancer Risks
The International Agency for Research on Cancer and the US National Institutes of Health have both issued strong warnings of the carcinogenic effect of acetaldehyde on humans and the heightened risk that exist for ALDH2 deficient individuals.[13][14]
The body of research around acetaldehyde and its links to various cancers is abundant.
Some examples include cancers of the:
Mental Impairment
Some researchers have also suggested that acetaldehyde exposure can lead to some of the behavioral and physiological effects previously attributed to alcohol, such as a reduction in coordination, memory impairment and tiredness.[20] Whilst research on this matter is contested and somewhat inconclusive, the findings remain pertinent in terms of the possible day to day effects of having too much exposure to the toxin.
Are Some People at More Risk Than Others?
The risks of acetaldehyde exposure discussed above apply to everyone. However, the degree to which they apply can vary from person to person depending on the efficiency with which their body is able to break down acetaldehyde into a non-toxic and easily excretable form. As discussed earlier in the article, the way in which our bodies do this is via a process called aldehyde dehydrogenase.
As discussed in our article about ALDH2 deficiency, some individuals possess a mutated gene that causes a deficiency in their ability to break down acetaldehyde. Whilst genetic testing is the most accurate and only truly reliable way to determine whether someone is affected by this mutation, one indication is if someone suffers a red face when they get alcohol.
This red face from alcohol is a histamine reaction to the acetaldehyde that was not broken down into a non-toxic and easily excretable form. Individuals who get this can be said to most likely possess the gene mutation that causes the body to be bad at breaking down acetaldehyde and thus would be more at risk in terms of the health risks discussed above.
Read more about this in our article about ALDH2 deficiency.
How To Remove Acetaldehyde From Body Naturally: What Science Says
Now we will discuss various ways that are commonly being used to help the body break down acetaldehyde and minimise the various health risks discussed above.
Reduce Acetaldehyde Exposure
The body can be aided significantly by reducing the amount of acetaldehyde it is required to break down at any given time. For example, many alcoholic beverages, such as white wine, are known to contain large amounts of acetaldehyde. When combining the acetaldehyde from the wine with the acetaldehyde that is produced during the metabolism of the wine’s alcohol, the result is a heavy load of toxins that the body is required to break down.
Couple this with an ALDH2 deficient liver and we have a situation where a large dose of acetaldehyde begins to contribute to some of the health risks discussed above. Moreover, if we increase the quantity to 3 glasses of wine instead 1 and increase the regularity of the exposure to 3 times a week, the risks begin to multiply very quickly.
The same logic applies to the various other environmental sources of acetaldehyde discussed in this article. The amount and regularity of exposure to the various sources of acetaldehyde in the environment will directly affect the severity of the risks discussed.
Therefore, becoming more conscious of the sources of acetaldehyde and reducing exposure to these sources can help the body break down acetaldehyde by reducing the amount it has it break down and, importantly, the amount that slips through the cracks and makes it into the blood.
Glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide made up of three amino acids (cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine). It is present in most mammalian tissue and acts as an antioxidant, scavenger of free radicals and a powerful detoxifying agent.[21] The cysteine component of glutathione has been shown to reduce acetaldehyde in the stomach after alcohol consumption.[22]
Glutathione is produced naturally by the human body, however is depleted rapidly when alcohol is consumed.[23] Boosting glutathione levels prior to and after alcohol consumption may work to counteract this depletion and restore the body’s ability to naturally break down acetaldehyde before it reaches the blood.
Unfortunately, glutathione supplementation is problematic in terms of its bioavailability when taken orally.
NAC
NAC, or N-Acetyl-Cysteine, is an amino acid that breaks down quickly into Glutathione and is also a prerequisite co-factor for the body’s natural production of glutathione. Unlike glutathione supplementation, NAC supplementation is more bio-available and a more effective way to increase the body’s natural glutathione levels than direct supplementation of glutathione itself.
NAC has also been studied in combination with alcohol. Results show that, in addition to helping increase the body’s natural production of glutathione, NAC also bind directly to acetaldehyde in the stomach before it can make its way into the blood stream.[24]
Quercetin
Quercetin is a flavonol found in many grains, leaves, vegetables and fruits. Studies have shown that quercetin supplementation has can increase intracellular concentration of glutathione by approximately 50%.[25] As mentioned above, increasing the body’s glutathione levels can help break down acetaldehyde.
L-Theanine
L-theanine is an amino acid found in green tea. Japanese researchers have extensively studied the interaction of L-Theanine and alcohol. They found it to increase glutathione in the body by increasing the level of glutamate in the liver.[26] Increased glutathione levels allow the body to break down acetaldehyde more quickly and helps reverse the depletion of glutathione caused by alcohol consumption.
Sunset
The supplement Sunset combines NAC, Glutathione, Quercetin and L-Theanine to help the body break down acetaldehyde from alcohol and other environmental sources. The three ingredients are combined with other complimentary compounds to form a synergy that is more effective than the sum of its parts.
Closing Thoughts On How To Remove Acetaldehyde From Body Naturally
There you have it - everything you need to know regarding the natural, effective removal of acetaldehyde from the body. Follow our tips above and you'll help your body recover rapidly.
Our best advice? Invest in a supplement to help you break this toxin down. There are tons of supplements you can use to help you speed up this process - and if you struggle with breaking down this toxin when drinking alcoholic beverages, they are a no-brainer investment. Even if you just consume mild alcoholic beverages, don't take any chances - get a quality supplement like Sunset. You'll thank yourself the next time you drink alcohol.
References
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/mesh/68000079
[2] https://ncit.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCI_Thesaurus&ns=NCI_Thesaurus&code=C44328
[3] http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0000990
[4] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080468846004061
[5] https://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/aa72/aa72.htm
[6] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17590988
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12437324
[8] https://doi.org/10.1080/08958370304461
[9] http://www.npi.gov.au/resource/acetaldehyde
[10] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3124883/
[11] https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.25844
[12] https://www.nature.com/articles/nature25154
[13] https://www.iarc.fr/en/media-centre/pr/2009/pdfs/pr196_E.pdf
[14] https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/alcohol-flush-signals-increased-cancer-risk-among-east-asians
[15] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19190158
[16] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16103445
[17] http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23101985
[18] http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12439712
[19] http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21307158
[20] https://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/arh294/258-265.pdf
[21] https://ncit.nci.nih.gov/ncitbrowser/ConceptReport.jsp?dictionary=NCI_Thesaurus&ns=NCI_Thesaurus&code=C523
[22] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21143248
[23] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1930162/
[24] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8833231
[25] https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0891584901008127
[26] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16141543
Enjoy drinking again and get Sunset Alcohol Flush Support for
33% off while stocks last!
What’s inside?
We use a pharmacist-formulated blend of Glutathione, Dihydromyricetin, Cysteine, L-Theanine, & B Vitamins to stop alcohol flushing before it can begin.
Learn more
94% of people who try Sunset are satisfied with the results.











